Hello! I'm the owner of Fusubon.
This is the second in a series of papers often used in carbohydrate restriction. The title of the paper is "Intermittent high glucose enhances apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in culture," and it was written by the University of Udine in Italy.
A literal translation of the title would be "Intermittent hyperglycemia leads to cell death of umbilical vein endothelial cells."
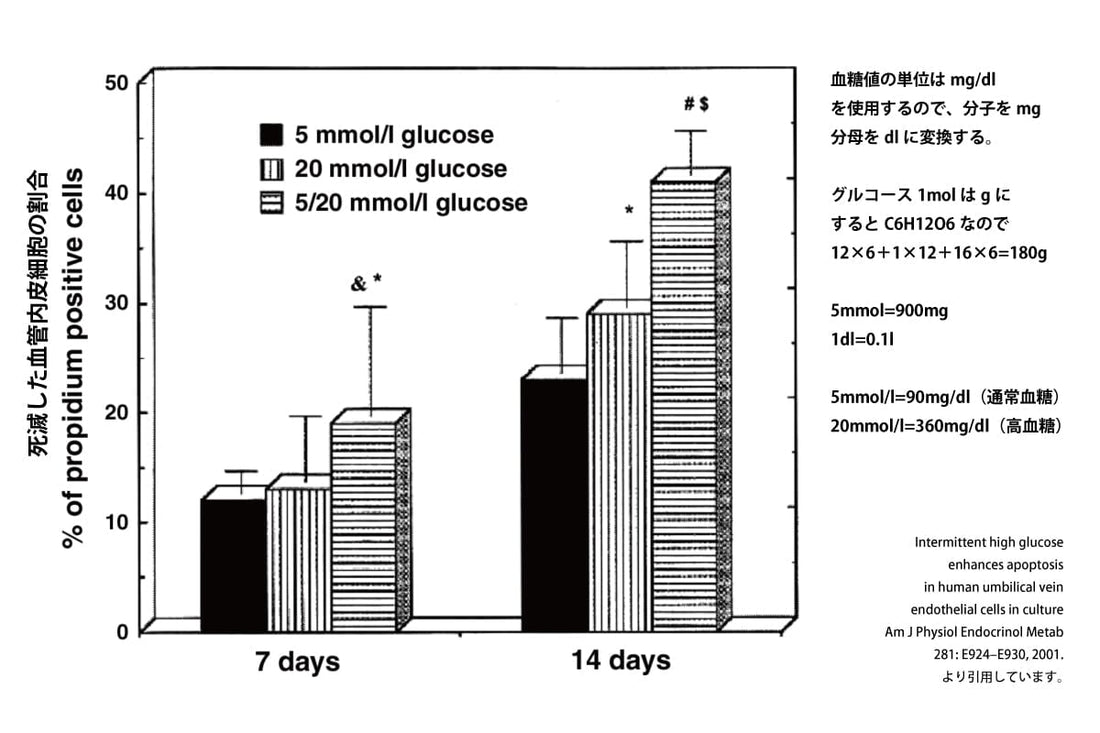
This paper conducted an experiment to examine the percentage of vascular endothelial cells that died over time under three conditions: "normal blood glucose levels," "high blood glucose," and "alternating exposure to normal and high blood glucose."
The less fluctuation in blood sugar levels, the less cell death there is.

Effects of blood glucose fluctuations on vascular endothelial cells
As the graph shows, cells die over time, even at normal blood sugar levels.
After seven days, the results showed that the percentage of dead cells was about 8 percent higher after one week in cells that had been alternately exposed to normal and high blood sugar compared to cells that had been constantly exposed to high blood sugar.
After 14 days, the difference widens to just under 20 percent.
What surprised me personally was that the rate of cell death was higher when blood sugar levels fluctuated than when blood sugar levels remained in a constant high blood sugar state .
This makes it hard to understand the point of using insulin to lower blood sugar levels.
Also, the title of the paper states that hyperglycemic conditions enhance cell death of umbilical vein endothelial cells, which I personally felt was a bit of a mismatch between the title and the content.
Postprandial hyperglycemia is the gateway to all diseases, including diabetes.

Metabolic Domino
Yutaka Ito What is the metabolic domino? A new way of looking at lifestyle-related diseases (explanation)
Quoted from Japanese Clinical Journal (0047-1852) Volume 61, Issue 10, Pages 1837-1843 (October 2003).
Diabetes is diagnosed when hemoglobin A1c is above 6% or fasting blood glucose is 110 mg/dl.
When we look back at the blood glucose levels of diabetic patients, we can see that abnormal fasting blood glucose levels occur several years before the patient is diagnosed with diabetes, but abnormal postprandial blood glucose levels occur about 10 years before the onset of diabetes.
As Dr. Ito Yutaka explains in his Metabolic Domino, research has shown that high blood sugar after meals is the root cause of all kinds of diseases, so be careful not to consume too much carbohydrates and make sure your blood sugar levels after meals are not abnormal.
Regular blood tests and post-meal blood glucose measurements
A blood test can only tell you hemoglobin A1c and blood sugar level at the time the blood is drawn.
There are devices available for easily measuring blood glucose levels at home, such as the Abbott blood glucose meter, so we recommend that you regularly measure your blood glucose levels after meals. See you next time!